Table of Contents
Dataset Introduction
Our dataset comprises a diverse collection of audio samples sourced from renowned databases like the Ryerson Audio-Visual Database of Emotional Speech and Song (RAVDESS), Toronto Emotional Speech Set (TESS), Surrey Audio-Visual Expressed Emotion (SAVEE), and Crowd Sourced Emotional Multimodal Actors Dataset (CREMA-D), augmented with audio features to enhance the model’s robustness across various demographics and contexts.
Data Compliance: The dataset aligns with General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), exemplifying adherence to the highest standards of data protection and privacy.
Privacy Considerations: Prioritizing privacy, the dataset is anonymization, safeguarding Personally Identifiable Information (PII) information. By meticulously removing personally identifiable details, the dataset ensures the utmost privacy for consumers.
Current Approach and Bottleneck Detection
Existing work in speech emotion recognition is facing several challenges, including variability in speech due to different languages, accents, and individual speaker characteristics. The emotional state can be subjective, leading to inconsistencies in labeled data. Limited availability of diverse, annotated datasets hinders training robust models. Furthermore, extracting relevant features from raw audio that accurately capture emotional nuances is complex. There’s also the need for models to perform well in real-world, noisy environments, which can degrade recognition accuracy.

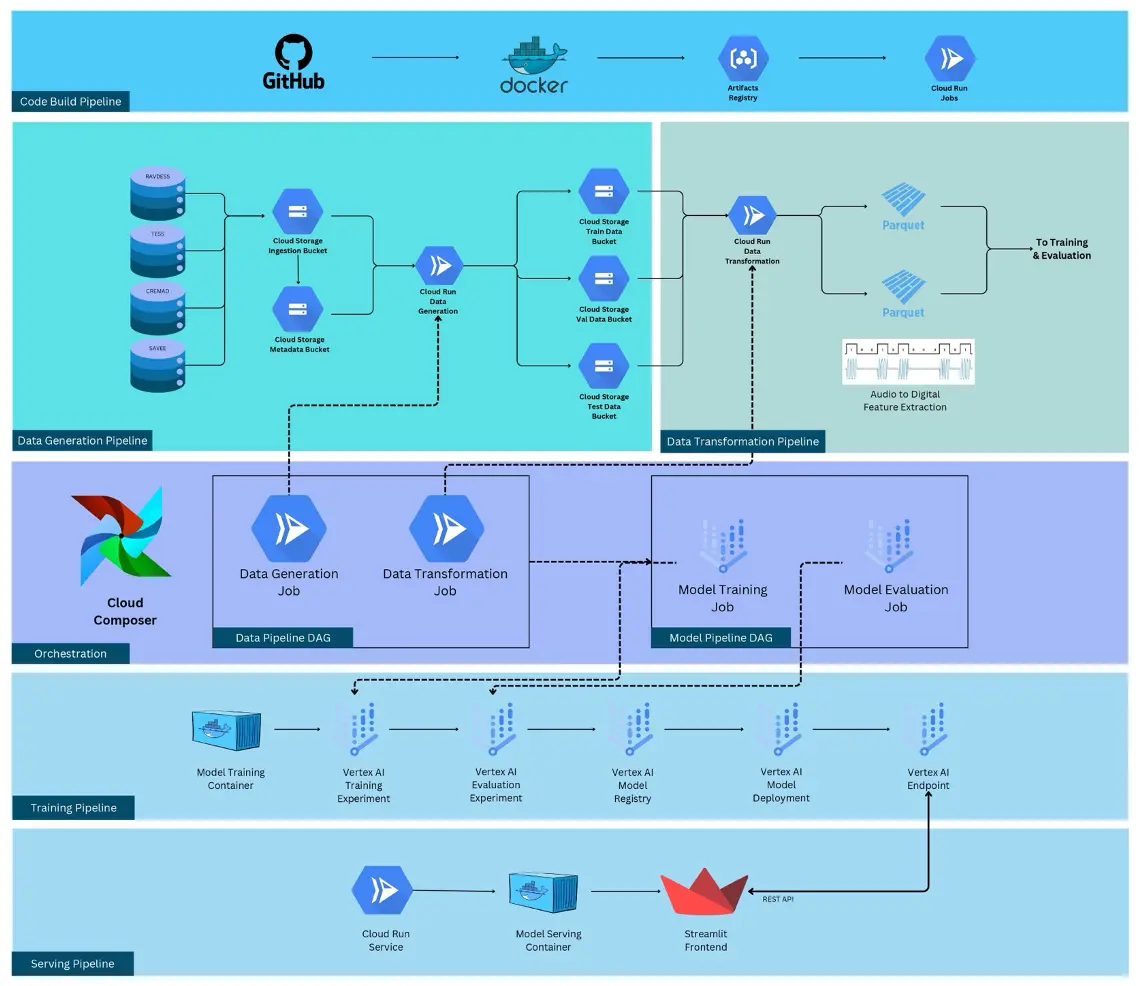
The current approach for the Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) MLOps project involves a data transformation stage that extracts audio features such as Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients (MFCC), Spectrogram, Zero Crossing Rate, and more. This step is crucial for preparing the audio data for model training and inference. However, it is also the main bottleneck in terms of time and resources. To address this bottleneck, the project utilizes Google Cloud Platform services leveraging its robust, scalable infrastructure to manage and deploy applications efficiently. Cloud Composer is used for Airflow orchestration of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), ensuring the smooth execution of the workflow tasks. Cloud Run is employed for running tasks in the pipeline, including data preparation, transformation, and model training, providing scalability and flexibility. Additionally, Vertex AI is used for model training, deployment, creation of a model endpoint, and monitoring, streamlining the machine learning operations. Despite these optimizations, the data transformation stage, even after using multi-processing, remains a significant challenge due to its time-consuming nature, highlighting the need for further optimization and efficiency improvements in this area.
Metrics, Objectives, and Business Goals
Business Goals
Implementing Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) for customer service in a tech company can significantly enhance business operations and user satisfaction. Accurate SER enables personalized customer interactions, optimizing service quality and efficiency. It aids in timely identifying and addressing customer frustrations, improving resolution rates.
Additionally, SER contributes to staff training by highlighting effective communication patterns. Data-driven insights from SER analytics can further refine customer engagement strategies, ensuring a consistently positive experience and fostering brand loyalty. This innovative approach aligns with modern expectations for empathetic, responsive service, setting the company apart in competitive markets.
Objectives
The primary objective of this project is to develop and implement a machine learning pipeline to help recognize an emotion in a speech in real time. By leveraging advanced machine learning and deep learning models, in a cloud-based machine learning platform. The accuracy of the methodology used to classify a speech into its respective emotion is the main focus of this project.
Success Metrics
This project is focused on SER, incorporating Continuous Training (CT), alongside CI/CD, Continuous Monitoring (CM), and dynamic dashboards for real-time metrics, the success criteria can be streamlined as follows:
- Automated CI/CD and Continuous Training (CT) Workflow:
- Efficient automation of data ingestion, model retraining, evaluation, and deployment processes to adapt to new audio files and speeches.
- Seamless integration and deployment of updates with minimal manual effort, ensuring the model stays current with the latest data and algorithms.
- Continuous Monitoring (CM) and Dashboards:
- Effective real-time monitoring of model performance (e.g., forecasting accuracy) and operational metrics (e.g., latency, throughput).
- Interactive dashboards that provide insights into model health, data quality, and the impact of weather on energy consumption.
- Automated alerts for model drift, data anomalies, or performance degradation, prompting timely adjustments.
- Model and Data Management:
- Robust version control for models and datasets, enabling traceability and quick rollback if needed.
- High-quality data ingestion and preprocessing to ensure accurate and reliable classifications.
- Scalability and Efficiency:
- Scalable architecture to handle varying volumes of audio files and formats.
- Optimized resource management, balancing computational costs with classification accuracy and timeliness.
- Adaptability and Continuous Improvement:
- Flexibility to incorporate new audio sources, new audio formats that require new ETL processes.Commitment to iterative improvement through regular feedback loops and model updates.
Success in this context is defined not just by technical robustness but also by the model’s ability to deliver actionable insights, drive operational efficiencies, and adapt to evolving data landscapes and business needs.
Deployment Infrastructure